Steam Transportation : Removal of Air and CO2
1. Air Removal
When starting operation of steam equipment and steam main, it is necessary to remove air first.
The steam trap which sets condensate removal as the 1st purpose has a great difference in exhaust capability by the operation principle used.
If exhaust capability is small, starting will take long time.
Air becomes a problem also not only during the time of starting operation but during operation.
Although steam contains usually a small amount of air, it is accumulated into equipment during its operation.
If steam condenses on heat transfer surface of equipment, since a small amount of air contained is not condensable, it is left on the surface.
As new steam condenses one after another, air is added, and then an air film is formed on the surface.
Since the thermal conductivity of air is about twentieth part of water, an air film becomes a serious obstacle of the thermal conductivity.
Furthermore, if air mixes into steam, its temperature falls than the saturation temperature of its pressure.
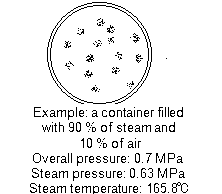
For example, steam temperature for pressure of 1.0MPa is 183.2 ℃. When 10% of air (by the capacity ratio) is included, it becomes 0.9 time of absolute pressure of 1.1MPa A (saturation temperature of 178.6 ℃ for absolute pressure of 0.99MPa A) and falls by 4.6 ℃.
If air is accumulated more and becomes 35%, temperature falls by 18.2 ℃ and the output of equipment declines greatly.
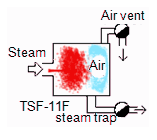
In order to operate equipment efficiently, this impeditive air is required to be removed. For this purpose, use an air vent.
An air vent is equipment which detects the fall of steam temperature caused by air mixing, and discharges it automatically.
Since it does not have the capability to separate steam and air, the mixture of steam and air is discharged.
Temperature fall by Air Mixing in Steam
| Support Intervals of Transverse Pipes (SHASE-010) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piping Diameter(A) | 15-20 | 25-32 | 40-80 | 90-150 | 175 or more |
| Intervals[m] | 1.8 or below | 2.0 or below | 3.0 or below | 4.0 or below | 5.0 or below |
| Pressure MPa/G | Air Mixing Rate in Steam (Volume) % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | |
| 0.1 | 119.6 | 118.8 | 118.3 | 117.2 | 116.3 | 115.4 | 114.5 |
| 0.2 | 132.9 | 131.7 | 130.5 | 129.3 | 128.1 | 126.7 | 125.4 |
| 0.3 | 142.9 | 141.4 | 139.9 | 138.4 | 136.9 | 135.4 | 133.9 |
| 0.4 | 151.1 | 149.5 | 147.8 | 146.2 | 144.6 | 142.6 | 140.9 |
| 0.5 | 158.1 | 156.3 | 154.6 | 152.8 | 151.1 | 149.1 | 147.9 |
| 0.6 | 164.2 | 162.3 | 160.5 | 158.7 | 156.7 | 154.6 | 151.8 |
| 0.7 | 169.6 | 167.7 | 165.8 | 163.9 | 161.7 | 159.6 | 157.4 |
| 0.8 | 174.5 | 172.6 | 170.2 | 168.5 | 166.3 | 164.2 | 161.7 |
| 0.9 | 179.0 | 177.0 | 174.5 | 172.8 | 170.2 | 168.3 | 165.8 |
| 1.0 | 183.2 | 181.1 | 179.0 | 176.8 | 174.5 | 172.1 | 169.6 |
| 1.2 | 190.7 | 188.5 | 186.3 | 184.0 | 181.5 | 179.0 | 176.3 |
| 1.4 | 197.4 | 195.1 | 192.8 | 190.3 | 187.8 | 185.1 | 182.4 |
| 1.6 | 203.4 | 201.0 | 198.6 | 195.9 | 193.4 | 190.7 | 187.8 |
| 1.8 | 208.8 | 206.4 | 203.9 | 201.3 | 198.6 | 196.0 | 192.8 |
| 2.0 | 213.8 | 211.4 | 208.8 | 206.2 | 203.4 | 200.4 | 197.4 |
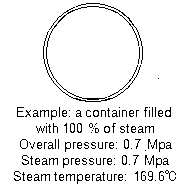
The container filled with the mixture of steam and air will transmit not the heat quantity in the total pressure but the heat quantity equivalent to the partial pressure of steam by the mixture ratio.
2. CO2 Gas Removal
If the water disposal of boiler feeding is not perfect, carbon dioxide generates inside the boiler and is emitted with steam.
Since strong corrosiveness is shown when this carbon dioxide dissolves in water, it is necessary to consider to discharge it at saturated vapor temperature.
Especially, prior to stopping the operation of equipment, fully blow and remove it.
Otherwise, when temperature falls after stopping, it dissolves in water and corrode equipment and trap.
Advice
Where does air gather?
Air always gathers at a place where there are few flows of steam and condensate.
Therefore, it changes with the positions of the steam inlet, and position of the condensate outlet in the equipment.
Please check the structure of equipment once again and reconsider the attachment position of air vent.